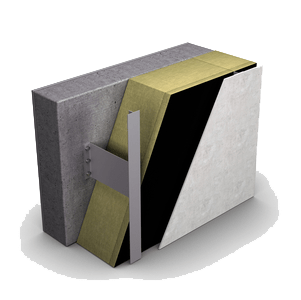
Available in a large variety, there are Paroc ventilated facade solutions for new buildings as well as renovations. Due to their fire properties, Paroc products can be used in ventilated wall structures. We offer solutions for wooden or metal frame buildings, masonry, or concrete walls, with one or two layers of insulation for various facade facings. Our wind protection product selection allows the choice of products for various types of buildings in different climate conditions and in compliance with different local regulations.
Furthermore, a ventilated façade can be designed either for new buildings or retrofit of existing buildings. It is important to check the general and local building regulations, especially in the area of structural, thermal, fire, and sound performance set for the materials, load bearing structures, or building envelope.
Navigate to local Paroc websites for more detailed information about ventilated facade solutions >
PAROC Stonewool is non-combustible and energy efficient insulation material to be used in all kind of ventilated façade systems. It is moisture resistant and is thus well suited for e.g. seaside resorts where the moisture stress on structures can be significantly higher than inland.